- Hadoop伪分布式配置教程
- 配置SSL证书后,Nginx的HTTPS 不能正常
- 【计算机毕业设计】023学生宿舍管理系统
- springboot集成Flink-CDC
- RabbitMQ清除积压消息管理界面出现 Unacked 消息
- 基于PHP和MySQL的新闻发布系统——【功能优化】
- 【计算机毕业设计】外卖点餐系统
- MySQL以及版本介绍
- 『赠书活动 | 第一期』《分布式中间件核心原理与RocketMQ最佳实
- 关于mysql配置文件的介绍
- (附源码)springboot学生宿舍管理系统毕业设计161542
- 数据库实验1 数据库定义与操作语言实验
- Windows系统上安装MySQL 5.7详细步骤
- 内网穿透实现在外远程连接RabbitMQ服务
- 关系型数据库(SQL)默认值操作
- 基于javaweb+mysql的jsp+servlet图书图书馆管理系
- 【计算机毕业设计】鲜花销售管理系统
- Go语言中的数组、切片和映射解析
- 瑞吉外卖项目 基于spring Boot+mybatis-plus开发
- MySQL数据库——MySQL REGEXP:正则表达式
- springboot:时间格式化的5种方法(解决后端传给前端的时间格式
- Java+Swing+MySQL实现学生选课管理系统
- MySQL之my.cnf配置文件
- nodejs升级引起的构建错误:0308010C:digital en
- 四步完全卸载 MySQL
- Spring Boot Web
- 【Spring Security】让你的项目更加安全的框架
- 最新版 nodejs和npm版本不匹配问题解决:ERROR: npm
- 10.网络爬虫—MongoDB详讲与实战
- 网上商城购物系统设计与实现(Java+Web+SSM+MySQL)
目录
1、前言
2、什么是Spring Event?
3、基本使用
3.1、定义事件
3.2、发布事件
3.3、监听事件
3.3.1、继承ApplicationListener
3.3.2、使用@EventListener注解
4、Spring Event是同步还是异步?
4.1、源码实现
4.2、如何实现异步
4.2.1、使用@Async注解
4.2.2、手动实现异步线程池
4.2.3、自定义ApplicationEventMulticaster
5、@TransactionalEventListener
5.1、基本使用
1、前言
事件发布/订阅机制在实际项目中很经常用到,一方面可以很容易让我们的代码进行解耦,另一方面可以很方便的进行一对一或一对多的消息通信,是一种常见的观察者设计模式,具有很好的扩展性。今天就来讲一下Spring的事件机制。
2、什么是Spring Event?
Spring框架中的事件是一种观察者设计模式的实现,用于在应用程序中处理各种状态变化。事件驱动编程是一种流行的编程范式,其中组件之间的通信是通过事件(或消息)进行的。Spring的事件机制允许对象在状态发生变化时发布事件,其他对象则可以订阅这些事件并在事件发生时执行特定的操作。
3、基本使用
Spring Event的使用基本有以下几个步骤:定义事件,发布事件,监听事件。
3.1、定义事件
先定义一个事件Event,继承Spring的ApplicationEvent,声明构造函数将需要传递的事件信息包装为业务事件类。如:
/**
* 这里定义事件DamIllegalDataEvent。
*/
public class DamIllegalDataEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
// 声明构造函数,接收DamIllegalDataDto集合传递到事件中
public DamIllegalDataEvent(List list) {
super(list);
}
}
3.2、发布事件
发布事件时可以注入ApplicationEventPublisher,也可以获取到ApplicationContext,然后调用publisherEvent()方法推送事件。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("anno/dam")
public class DamTestController {
@Autowired
private ApplicationEventPublisher applicationPushBuilder;
@GetMapping("test_audit")
public String test_audit(){
DamIllegalDataDto build = DamIllegalDataDto.builder().illegalData("11111").source("2222").functionDesc("数据清理中错误了").functionName("333").build();
// 注入applicationPushBuilder
applicationPushBuilder.publishEvent(new DamIllegalDataEvent(Collections.singletonList(build)));
// 这里也可以直接使用hutool工具类直接发布
SpringUtil.publishEvent(new DamIllegalDataEvent(Collections.singletonList(build)));
return "ok";
}
}
3.3、监听事件
监听事件也可称为订阅事件,即当事件发布了之后,需要监听该事件并进行消费。Spring里面提供了两种事件订阅的方式:
- 继承ApplicationListener,并实现onApplicationEvent方法。
- 使用@EventListener注解方法。
3.3.1、继承ApplicationListener
创建一个监听器DamIllegalDataEventListener继承ApplicationListener,通过泛型指定需要监听的事件类。如:
@Slf4j @Component public class DamIllegalDataEventListener implements ApplicationListener
{ @Autowired private DamIllegalDataAuditService damIllegalDataAuditService; @Override public void onApplicationEvent(DamIllegalDataEvent event) { LOGGER.info("异常数据审计事件开始执行..."); List damIllegalDataDtos = (List ) event.getSource(); // todo...... doSomething(); } } 3.3.2、使用@EventListener注解
使用@EventListener注解方法,将其包装为事件处理器。它适用于:1. 不想为每个事件处理都创建一个ApplicationListener实现类;2. 希望支持更复杂的事件条件过滤。@EventListener的classes属性可以过滤事件类型,而condition属性可以根据事件对象是否满足条件表达式来过滤事件。
@Slf4j @Component public class DamIllegalDataEventListener { /** * EventListener注解定义事件处理器,并指定监听事件为DamIllegalDataEvent。 * condition声明只有事件的code==200时,才进入该事件 */ @EventListener(classes = {DamIllegalDataEvent.class}, condition="#event.code==200") public void onApplicationEvent(DamIllegalDataEvent event) { LOGGER.info("异常数据审计事件开始执行..."); ListdamIllegalDataDtos = (List ) event.getSource(); // todo...... doSomething(); } } 4、Spring Event是同步还是异步?
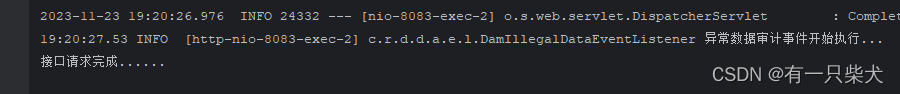
默认情况下 Spring Event是同步执行的。你怎么这么确定?我们先来演示下上面的demo。先实现一个测试接口,该接口发布了一个事件,发布完后打印一行日志:
@GetMapping("test_audit") public String test_audit(){ DamIllegalDataDto build = DamIllegalDataDto.builder().illegalData("11111").source("2222").functionDesc("数据清理中错误了").functionName("333").build(); SpringUtil.publishEvent(new DamIllegalDataEvent(Collections.singletonList(build))); System.out.println("接口请求完成......"); return "ok"; }事件监听中打印一行日志,并睡眠5s:
@Slf4j @Component public class DamIllegalDataEventListener implements ApplicationListener
{ @Override public void onApplicationEvent(DamIllegalDataEvent event) { LOGGER.info("异常数据审计事件开始执行..."); ThreadUtil.sleep(5000); } } 执行查看结果,可以发现不管如何请求,日志打印总是按顺序执行,并且会间隔5S。
4.1、源码实现
如果还是不信?那我们来看源码:org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher#publishEvent(java.lang.Object),断点跟进到org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#publishEvent(java.lang.Object, org.springframework.core.ResolvableType)。
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) { // 包装ApplicationEvent ApplicationEvent applicationEvent; if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) { applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event; } else { applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event); if (eventType == null) { eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent) applicationEvent).getResolvableType(); } } // 考虑到部分事件在Listener注册之前就发布了,因此先保存起来 if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) { this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent); } else { // 重点是这里 // 铜通过getApplicationEventMulticaster()获取事件发布器; // 调用multicastEvent方法发布事件 getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType); } // 同时给父容器发布事件 if (this.parent != null) { if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) { ((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType); } else { this.parent.publishEvent(event); } } }跟进multicastEvent()方法,org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster#multicastEvent(org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent, org.springframework.core.ResolvableType):
@Override public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) { ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event)); Executor executor = getTaskExecutor(); for (ApplicationListener listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) { // 这里可以看出,如果有指定任务执行器,那么就异步执行;否则直接调用,也就是同步执行。 if (executor != null) { executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event)); } else { invokeListener(listener, event); } } }4.2、如何实现异步
实现异步方式,可以有3中实现:
- 使用@Async 注解
- 手动实现异步线程池
- 自定义ApplicationEventMulticaster
4.2.1、使用@Async注解
使用这个很简单,只要在事件监听方法上添加@Async注解即可,springboot的启动器需要开启异步@EnableAsync。
@Async @Override public void onApplicationEvent(DamIllegalDataEvent event) { LOGGER.info("异常数据审计事件开始执行..."); ThreadUtil.sleep(5000); }
注意:
使用@Async时,最好自己配置相应的线程池核心数以及延迟队列等等。由于Spring中使用@Async异步线程每次都会创建一个新线程执行,如果滥用 它,可能会有内存问题。
4.2.2、手动实现异步线程池
顾名思义就是手动创建一个线程池执行,与@Async类似。
@Slf4j @Component public class DamIllegalDataEventListener implements ApplicationListener
{ @Override public void onApplicationEvent(DamIllegalDataEvent event) { ThreadUtil.execAsync(() -> { LOGGER.info("异常数据审计事件开始执行..."); ThreadUtil.sleep(5000); }); } } 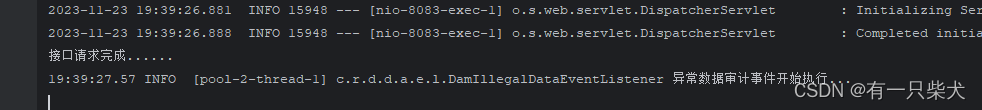
4.2.3、自定义ApplicationEventMulticaster
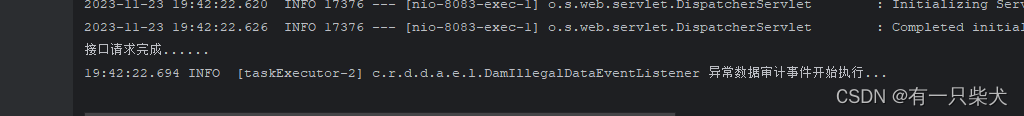
由于Spring容器会优先使用beanName为applicationEventMulticater 的bean作为事件转发处理器,如果不存在则默认使用SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster作为事件转发处理器,它默认是同步执行的。但它支持设置Executor,那么我们可以将自定义的线程池处理器作为Executor,以此来支持异步执行。
@Configuration public class DamEventConfig { @Bean(AbstractApplicationContext.APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME) public SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster eventMulticaster(){ SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster simpleApplicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(); simpleApplicationEventMulticaster.setTaskExecutor(taskExecutor()); return simpleApplicationEventMulticaster; } /** * 目前服务器为8c,默认给他4个,一般事件推送的情况不会多。如果多的话,请检查一下业务使用 * @return */ @Bean public TaskExecutor taskExecutor(){ ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor(); executor.setCorePoolSize(4); return executor; } }配置完之后,事件监听那边都无需修改。
注意:
这种方式的配置是全局性的,一旦配置了之后,所有的事件都是异步的形式处理。如果需要个别业务是同步的,那么此种方式要特别注意。
5、@TransactionalEventListener
提到事件,这里再提一个注解@TransactionalEventListener,也即感知事务,基于事件形式与事务的某个阶段进行绑定。比如在事务提交之前或之后进行一些业务的处理,如短信提醒等等。@TransactionEventListener允许事件处理方法感知事务。它的phase属性,表示希望在事务的哪个阶段执行事件处理。
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @EventListener public @interface TransactionalEventListener { /** * Phase to bind the handling of an event to. *The default phase is {@link TransactionPhase#AFTER_COMMIT}. *
If no transaction is in progress, the event is not processed at * all unless {@link #fallbackExecution} has been enabled explicitly. */ TransactionPhase phase() default TransactionPhase.AFTER_COMMIT; /** * Whether the event should be handled if no transaction is running. */ boolean fallbackExecution() default false; /** * Alias for {@link #classes}. */ @AliasFor(annotation = EventListener.class, attribute = "classes") Class[] value() default {}; /** * The event classes that this listener handles. *
If this attribute is specified with a single value, the annotated * method may optionally accept a single parameter. However, if this * attribute is specified with multiple values, the annotated method * must not declare any parameters. */ @AliasFor(annotation = EventListener.class, attribute = "classes") Class[] classes() default {}; /** * Spring Expression Language (SpEL) attribute used for making the event * handling conditional. *
The default is {@code ""}, meaning the event is always handled. * @see EventListener#condition */ @AliasFor(annotation = EventListener.class, attribute = "condition") String condition() default ""; /** * An optional identifier for the listener, defaulting to the fully-qualified * signature of the declaring method (e.g. "mypackage.MyClass.myMethod()"). * @since 5.3 * @see EventListener#id * @see TransactionalApplicationListener#getListenerId() */ @AliasFor(annotation = EventListener.class, attribute = "id") String id() default ""; }
TransactionPhase枚举声明了事务提交的各个阶段:
public enum TransactionPhase { /** * Handle the event before transaction commit. * @see TransactionSynchronization#beforeCommit(boolean) */ BEFORE_COMMIT, /** * Handle the event after the commit has completed successfully. *Note: This is a specialization of {@link #AFTER_COMPLETION} and therefore * executes in the same sequence of events as {@code AFTER_COMPLETION} * (and not in {@link TransactionSynchronization#afterCommit()}). *
Interactions with the underlying transactional resource will not be * committed in this phase. See * {@link TransactionSynchronization#afterCompletion(int)} for details. * @see TransactionSynchronization#afterCompletion(int) * @see TransactionSynchronization#STATUS_COMMITTED */ AFTER_COMMIT, /** * Handle the event if the transaction has rolled back. *
Note: This is a specialization of {@link #AFTER_COMPLETION} and therefore * executes in the same sequence of events as {@code AFTER_COMPLETION}. *
Interactions with the underlying transactional resource will not be * committed in this phase. See * {@link TransactionSynchronization#afterCompletion(int)} for details. * @see TransactionSynchronization#afterCompletion(int) * @see TransactionSynchronization#STATUS_ROLLED_BACK */ AFTER_ROLLBACK, /** * Handle the event after the transaction has completed. *
For more fine-grained events, use {@link #AFTER_COMMIT} or * {@link #AFTER_ROLLBACK} to intercept transaction commit * or rollback, respectively. *
Interactions with the underlying transactional resource will not be * committed in this phase. See * {@link TransactionSynchronization#afterCompletion(int)} for details. * @see TransactionSynchronization#afterCompletion(int) */ AFTER_COMPLETION }
5.1、基本使用
在含有事务的方法里发布事件:
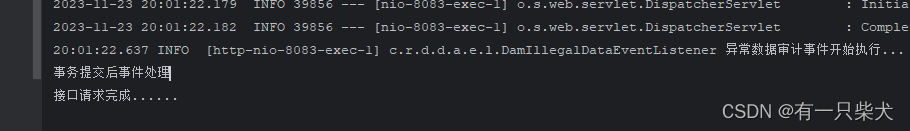
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class) public void test(){ DamIllegalDataAudit audit = new DamIllegalDataAudit(); audit.setId("1726931543097610240"); audit.setRemark("xxx"); this.baseMapper.updateById(audit); DamIllegalDataDto build = DamIllegalDataDto.builder().illegalData("11111").source("2222").functionDesc("数据清理中错误了").functionName("333").build(); applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(new DamIllegalDataEvent(Collections.singletonList(build))); }定义感知事务监听:
@Component public class TransactionalEventProcess { @TransactionalEventListener(phase = TransactionPhase.AFTER_COMMIT) public void afterCommit(DamIllegalDataEvent event){ System.out.println("事务提交后事件处理"); } @TransactionalEventListener(phase = TransactionPhase.AFTER_ROLLBACK) public void afterRollback(DamIllegalDataEvent event){ System.out.println("事务回滚后事件处理"); } }当执行事务方法时候,可以发现:
注意:
如果事件自定义了ApplicationEventMulticaster,让事件变成异步,那么该感知事务会失效。
但是如果使用@Async或手动定义了 异步线程池ThreadUtil.execAsync还是可以生效的。














