- 数据库实训sqlserver
- 在Portainer创建Nginx容器并部署Web静态站点实现公网访问
- mysql -- 左连接一对多只取一条,去重重复字段
- SpringCloud Alibaba(一)微服务简介+Nacos的安
- (详细版)java实现小程序获取微信登录,用户信息,手机号,头像
- Go语言中的gin框架之【GETPOST】请求参数接收传值(五)
- Node.js安装教程
- Java+Swing+MySQL实现学生选课管理系统
- 如何搭建一个简单的springCloudAlibaba项目,并实现基本
- Vue项目的搭建和启动
- 在springBoot中使用JWT实现1.生成token,2.接收前端
- SQL Server中的NULL值处理:判断与解决方案
- 记录打包部署Springboot项目到Windows环境
- 【Spring Boot学习】日志文件,Spring Boot也会写日
- Spring Boot + MinIO 实现文件切片极速上传技术
- 云计算——虚拟化层架构
- (附源码)springboot宠物领养系统 毕业设计 241104
- mysql 命令行启动显示“服务名无效”
- 深入浅出Node.js中的node
- Docker的配置和部署,并搭建php和nginx环境
- 终极解决 mysql8.0 ERROR 1045 (28000): A
- mysql 存储过程
- MySQL 中的 JSON
- Java完整版(JavaSe语法,数据结构,Mysql,网络,Java
- SpringBoot项目启动成功但接口访问404
- 基于springboot的短视频网站的设计与实现 毕业设计开题报告
- Web项目部署环境搭建:JDK + Tomcat + IDEA +My
- MinIO安装配置访问以及SpringBoot整合MinIO
- com.mysql.jdbc.Driver 和 com.mysql.c
- Nginx 【location配置路径详解、反向代理、负载均衡】
文章目录
- 一.单文件下载
- 1.简单理解文件下载
- 2.单文件下载的具体代码实现
- 3.测试
- 4.单文件下载整体代码
- 二.多文件批量下载(多个文件合成一个压缩包下载)
- 1.多文件下载的实现方式,这里使用了ZipOutputStream
- 2.具体代码实现
- 3.测试
- 4.文件批量下载(多文件合成一个压缩包)完整代码
- 三.补充,将整个文件夹压缩
- 1.将一个文件夹压缩,这个文件夹中全是具体文件
- 2.将整个文件夹压缩,文件中包含文件夹
一.单文件下载
1.简单理解文件下载
文件下载,是从服务器下载到本地电脑。 文件下载的原理,首先通过IO流将服务器的文件读取到内存里(只有将数据读到内存,电脑才可以操作数据),读取后文件数据存放在内存中,将内存中的数据通过网络发送给本地客户端的浏览器。本地客户端的浏览器接受数据,并在本地生成对应的文件。

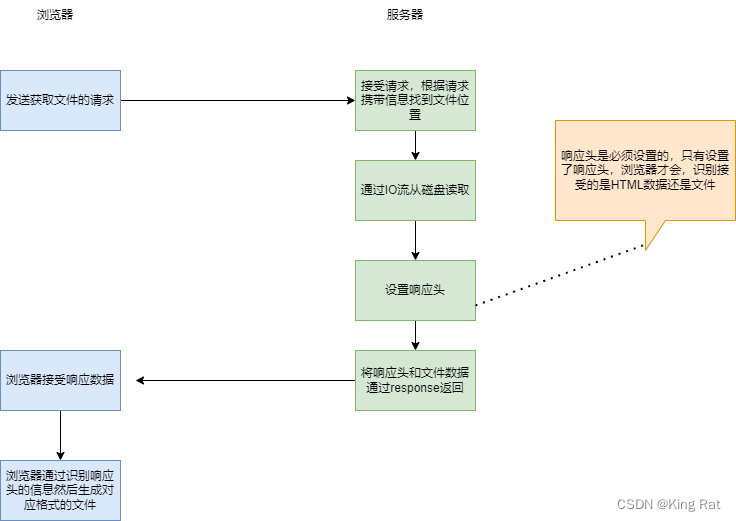
2.单文件下载的具体代码实现
- 接受请求,参数 path是文件在服务器的路径(通常路径会存在sql表里,通过查表获取,这里是为了测试),HttpServletResponse 要通过HttpServletResponse来实现客户端和服务器通信的响应部分(将响应头和文件数据返回后端)。
@RequestMapping("/download") public void downLoad(String path, HttpServletResponse response) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {- 设置响应头信息(规定死的)
响应头信息代表的含义:
- ContentType ,互联网媒体类型,也叫做MIME类型,Http在传输数据对象时会为他们打上MIME的数据格式标签,区分数据类型
常见ContentType,
- text/html ,HTML文本
- application/json , 键值对的json数据格式
- application/octet-stream ,是一种二进制数据流的文件类型,通常用于文件传输。它表示文件中包含的数据是二进制数据,而不是文本。由于它是一种通用类型,因此它可用于处理各种类型的文件,如图像,音频和视频文件。
- Content-Disposition
指定响应头的展示方式,主要体现在:
* 指定下载文件的文件名和保存方式。如"attachment; filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8")中的filename=xxx指定了后的文件的文件名和格式
* 控制浏览器的行为。如"attachment; filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8")的attachment,指定浏览器以附件的形式展示文件,即指定浏览器下载文件而不是打开文件,如果设置为inline,则是在浏览器打开文件。如果没有filename 浏览器会出现保存为的对话框。
- 常见值
Content-Disposition: inline Content-Disposition: attachment Content-Disposition: attachment; filename="XXX"
* 设置响应头代码
response.reset(); response.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment; filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8")); response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");//设置编码格式为utf-8 response.setContentLength((int)file.length());//响应数据长度 response.setContentType("application/octet-stream");-
通过IO流读取文件并将数据返回给浏览器
try(BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));OutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();)是try-with-resource的语法格式,作用为try块退出时,会自动调用在()中的bis,outputStream资源的close()方法,自动关闭IO资源。(不用手动关闭了代码书写复杂度降低)
获取response的输出流OutputStream,从文件的InputStream输入流读取数据到内存,然后通过输出流写入。
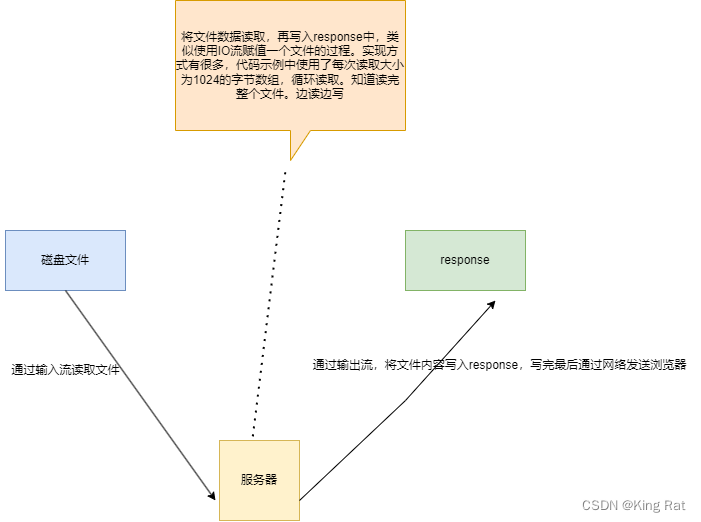
- 代码示例
try(BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));OutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();) { byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int i=0; while((i=bis.read(bytes))!=-1) { outputStream.write(bytes,0,i); } }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }3.测试
4.单文件下载整体代码
@RequestMapping("/download") public void downLoad(String path, HttpServletResponse response) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { File file=new File(path); String fileName= file.getName(); response.reset(); response.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment; filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8")); response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); response.setContentLength((int)file.length()); response.setContentType("application/octet-stream"); System.out.println("filename:"+fileName); try(BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));OutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();) { byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int i=0; while((i=bis.read(bytes))!=-1) { outputStream.write(bytes,0,i); } }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }二.多文件批量下载(多个文件合成一个压缩包下载)
1.多文件下载的实现方式,这里使用了ZipOutputStream
- 介绍ZipOutputStream
-
ZipOutputStream使用流程,
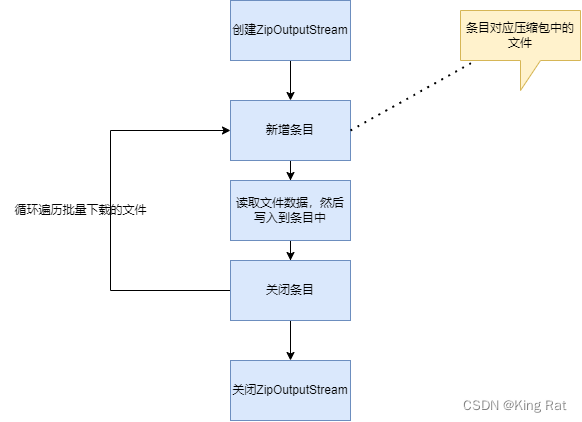
-
使用示例
//初始化,test.zip是写入压缩包的名称 ZipOutputStream zipOutputStream = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("test.zip")); //创建一个名称为test.txt新的条目,一般压缩包中有很多文件,新条目相当于创建新文件 zipOutputStream.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry("test.txt")); //写入具体内容 zipOutputStream.write("Hello World".getBytes()); //关闭条目 zipOutputStream.closeEntry(); //关闭整体压缩输出流 zipOutputStream.close();2.具体代码实现
- 模拟选中多文件(可以通过前端传)
List
pathList=new ArrayList<>(); pathList.add("xxx.txt"); pathList.add("xxx.txt"); pathList.add("xxx.txt"); - 设置响应头
response.reset(); response.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment; filename=" + URLEncoder.encode("1.zip", "UTF-8")); response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");- 初始化ZipOutputStream
try(ZipOutputStream zipOutputStream=new ZipOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(response.getOutputStream())))
- 遍历List,从中读取要批量下载的文件路径
for(String pathName:pathList)
- 对每个批量下载的文件,都在zipOutputStream(压缩包中创建对应的条目,及对应的文件)putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(fileName))创建和下载文件相同名称的文件条目。把每个下载的文件内容写入到zipOutputStream中的条目中,关闭条目,然后循环。
File file =new File(pathName); String fileName=file.getName(); zipOutputStream.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(fileName)); try(BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file))){ byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int i=0; while((i=bis.read(bytes))!=-1) { zipOutputStream.write(bytes,0,i); } zipOutputStream.closeEntry();3.测试

4.文件批量下载(多文件合成一个压缩包)完整代码
@GetMapping("/downloadlist") public void downLoadList( HttpServletResponse response ) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { ListpathList=new ArrayList<>(); pathList.add("xxx.txt"); pathList.add("xxx.txt"); pathList.add("xxx.txt"); response.reset(); response.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment; filename=" + URLEncoder.encode("1.zip", "UTF-8")); response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); response.setContentType("application/octet-stream"); try(ZipOutputStream zipOutputStream=new ZipOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(response.getOutputStream()))) { for(String pathName:pathList) { File file =new File(pathName); String fileName=file.getName(); zipOutputStream.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(fileName)); try(BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file))){ byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int i=0; while((i=bis.read(bytes))!=-1) { zipOutputStream.write(bytes,0,i); } zipOutputStream.closeEntry(); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } 三.补充,将整个文件夹压缩
1.将一个文件夹压缩,这个文件夹中全是具体文件
关键点在ZipOutputStream中的putNextEntry() 方法上,putNextEntry()相当于往压缩包中加入子文件(也可以是子文件夹),new ZipEntry(fileName)是建立的子文件(或文件夹),如果
- fileName为a.txt或xx.pdf相当于直接创建子文件放入压缩包
- fileName为ddd/a.txt 则会在压缩包中创建一个为ddd的文件夹,ddd文件夹下创建a.txt
zipOutputStream.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(fileName));
实际解决思路,如果要将一个文件夹下的多个文件压缩,实际效果为点开压缩包,里面有个文件夹,文件夹下是多个文件
解决,
- 创建一个压缩包,对应了new ZipOutputStream ,
- 有了这个压缩包,需要在创建压缩包里的文件,对应了new ZipEntry(fileName),若参数fileName带路径,则会创建带文件夹的文件
- 将创建的文件加入压缩包,putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(fileName))
- 将要文件数据写入到要压缩包中的文件中
总的来说是,操作每个文件的时候要保留前面文件夹的路径,fileName必须是ddd/a.txt,这样才会在压缩包中有文件夹
2.将整个文件夹压缩,文件中包含文件夹
解决,
判断是文件夹还是文件,如果是文件夹,则将文件夹名称记录传给子文件,如果是文件,传过来的文件夹和文件名,在压缩包中创建对应的文件夹名和文件名,然后将数据复制给压缩包中的文件
总的来说,压缩文件或文件夹是通过fileName参数在压缩包中创建文件夹或文件,然后将数据拷贝给压缩包中的文件一份

- 对每个批量下载的文件,都在zipOutputStream(压缩包中创建对应的条目,及对应的文件)putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(fileName))创建和下载文件相同名称的文件条目。把每个下载的文件内容写入到zipOutputStream中的条目中,关闭条目,然后循环。
- 遍历List,从中读取要批量下载的文件路径
- 初始化ZipOutputStream
- 设置响应头
- 模拟选中多文件(可以通过前端传)
-
- 介绍ZipOutputStream
- 代码示例
-
- ContentType ,互联网媒体类型,也叫做MIME类型,Http在传输数据对象时会为他们打上MIME的数据格式标签,区分数据类型
- 设置响应头信息(规定死的)
- 接受请求,参数 path是文件在服务器的路径(通常路径会存在sql表里,通过查表获取,这里是为了测试),HttpServletResponse 要通过HttpServletResponse来实现客户端和服务器通信的响应部分(将响应头和文件数据返回后端)。














